Partial Peptide of α-Synuclein Modified with Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Inhibits Amyloid Fibrillation of α-Synuclein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Proteolytic-Digested α-Synuclein Partial Peptide Sequence
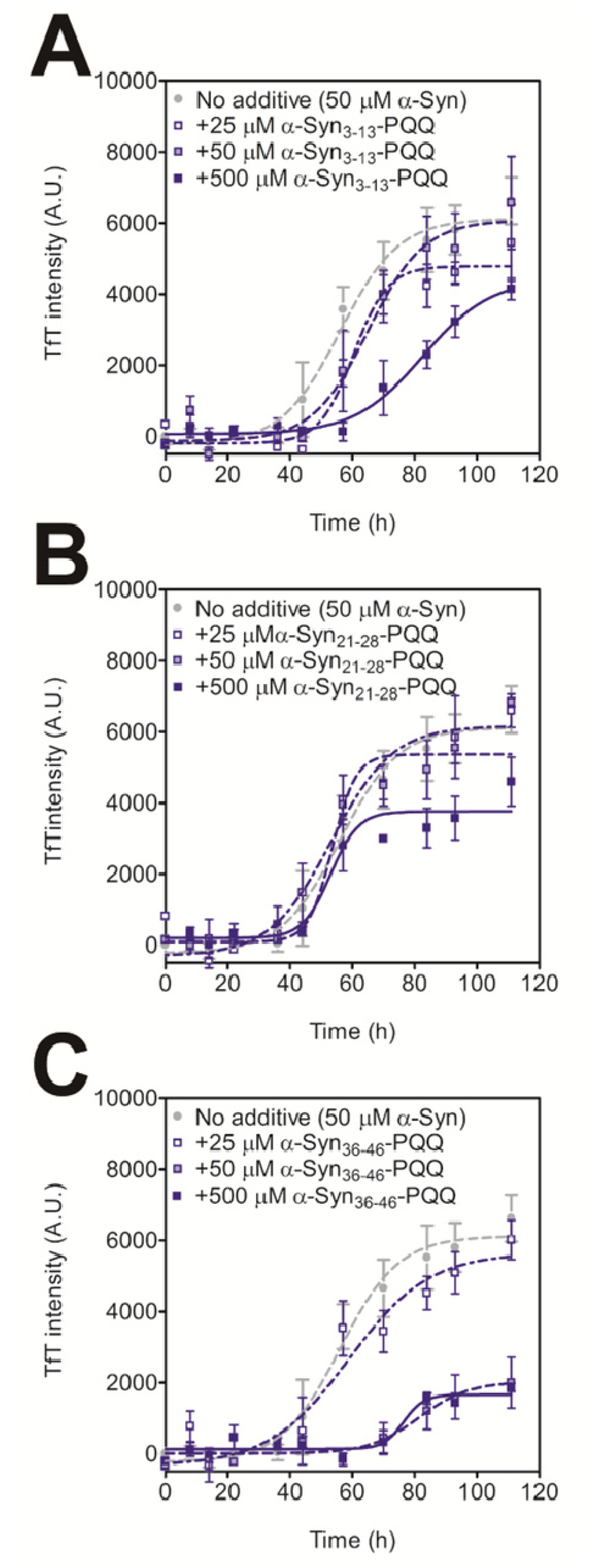
2.2. Evaluation of Inhibitory Effects of PQQ-Modified Peptides on Amyloid Formation of α-Synuclein
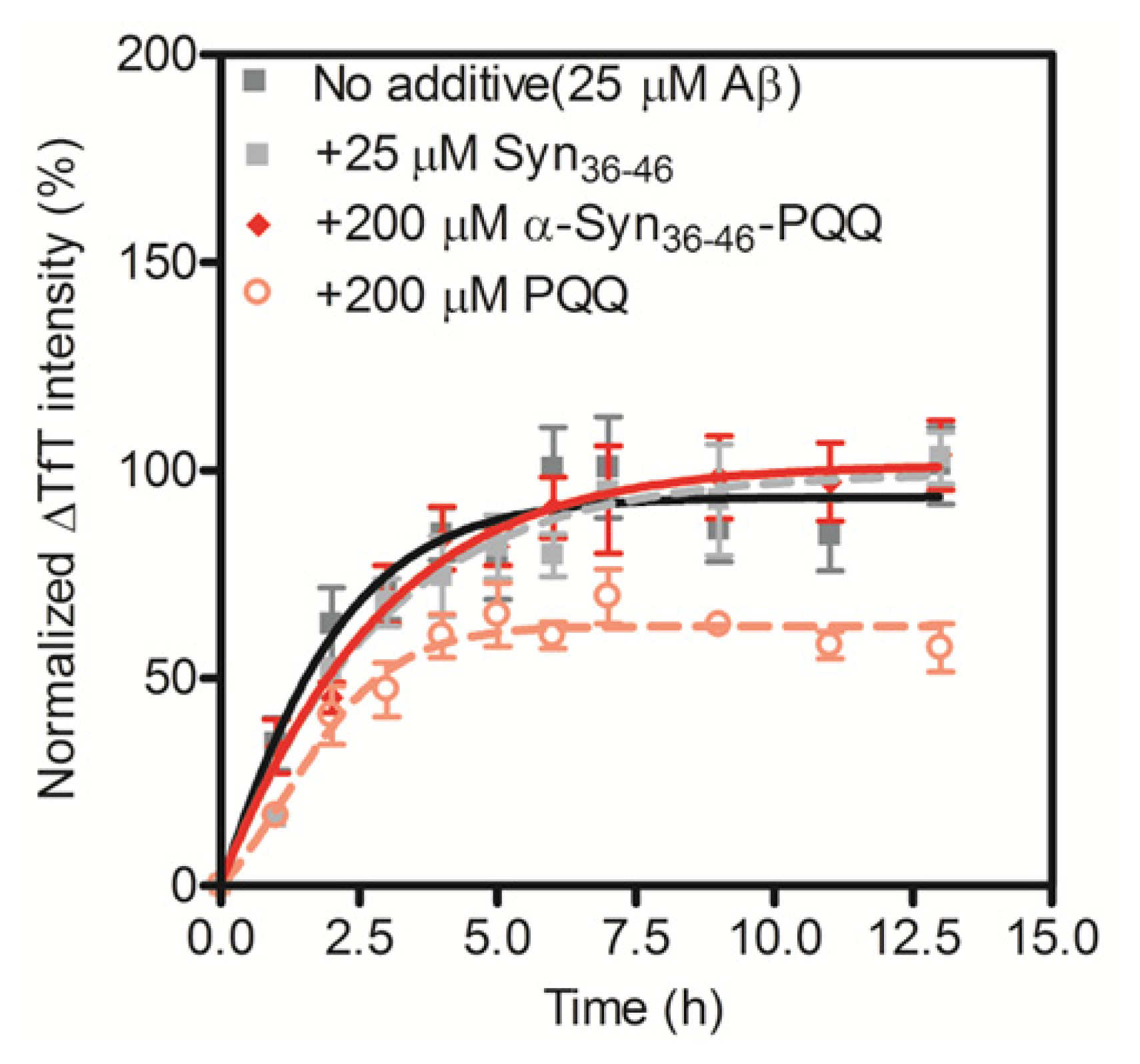
2.3. Evaluation of Specificity of PQQ-Modified α-Syn36–46 Peptide
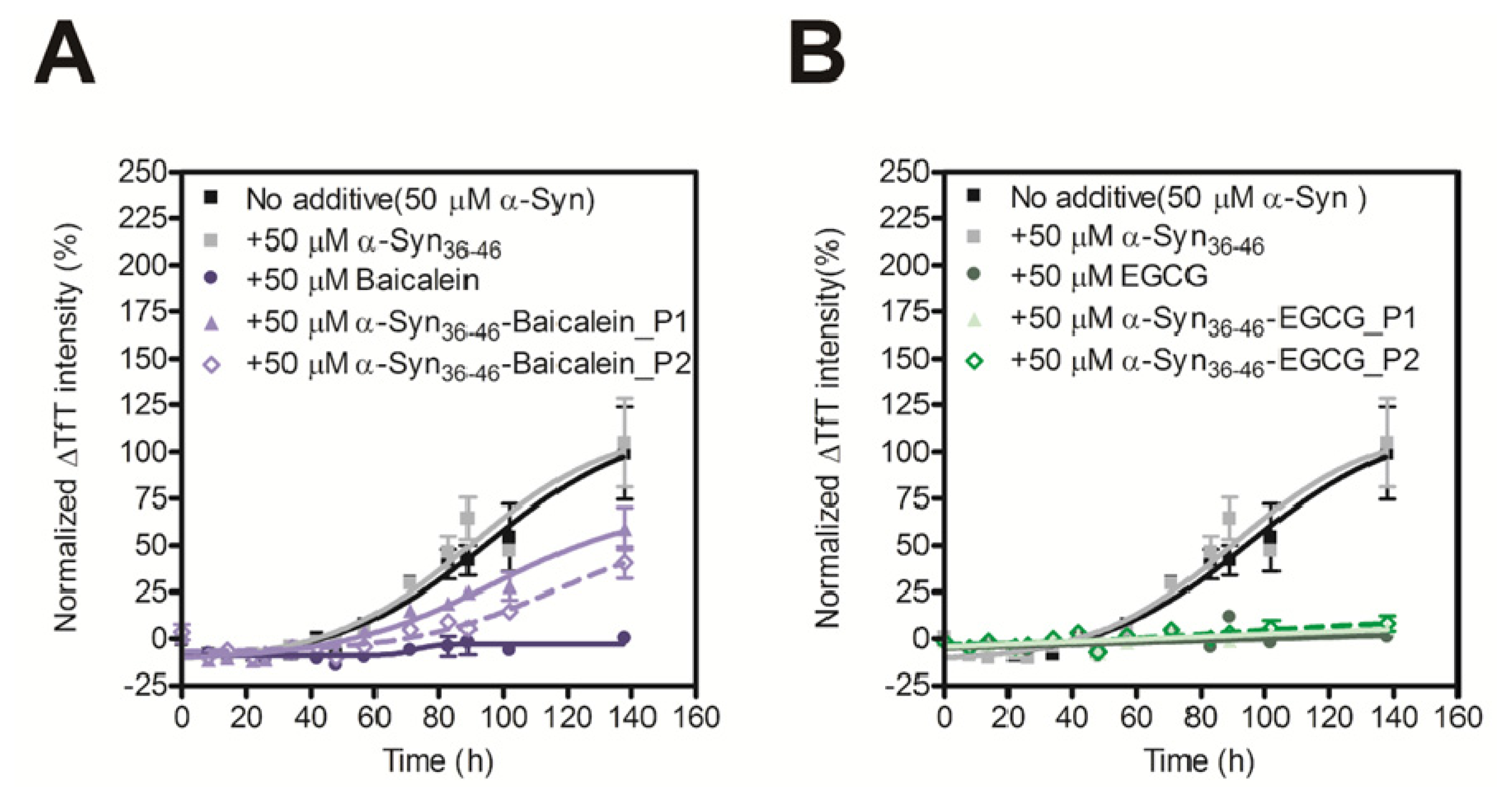
2.4. Evaluation of Inhibitory Effects of Baicalein or EGCG-Modified α-Syn36–46 Peptide on Amyloid Formation of α-Synuclein
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Recombinant α-Synuclein
3.2. LC/MS Analysis of Proteolytic-Digested α-Synuclein
3.3. PQQ, Baicalein, EGCG-Modification of α-Syn Partial Peptides
3.4. Amyloid Fibril Formation Analysis
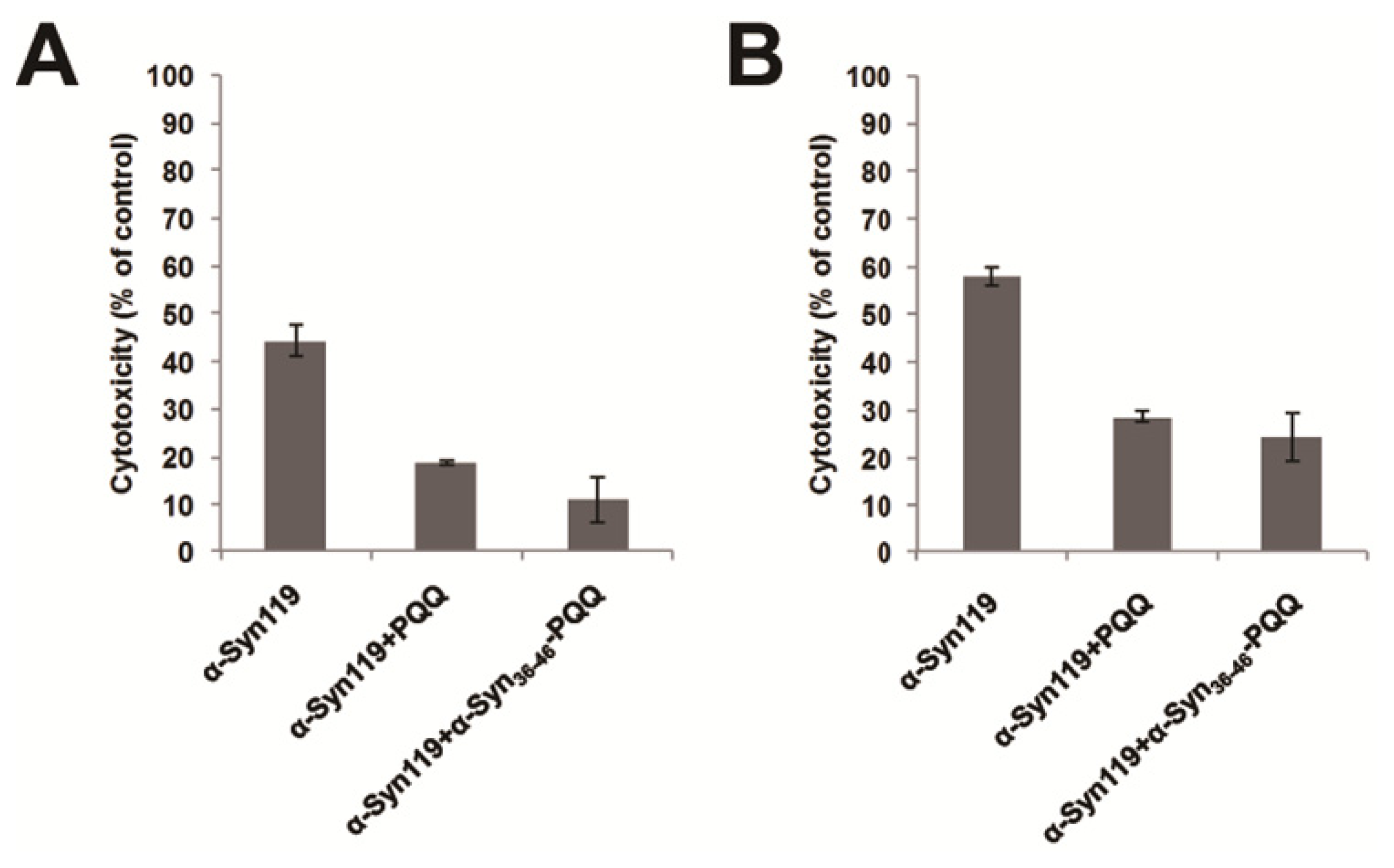
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay of α-Synuclein
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Eriksen, J.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Dickson, D.W.; Petrucelli, L. Caught in the act: alpha-synuclein is the culprit in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 2003, 40, 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Tofaris, G.K.; Spillantini, M.G. Alpha-synuclein dysfunction in Lewy body diseases. Mov. Disord 2005, 20, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2006, 314, 777–781. [Google Scholar]
- Lansbury, P.T.; Lashuel, H.A. A century-old debate on protein aggregation and neurodegeneration enters the clinic. Nature 2006, 443, 774–779. [Google Scholar]
- Sciarretta, K.L.; Gordon, D.J.; Meredith, S.C. Peptide-based inhibitors of amyloid assembly. Methods Enzymol 2006, 413, 273–312. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Bitan, G. Modulating self-assembly of amyloidogenic proteins as a therapeutic approach for neurodegenerative diseases: strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Med. Chem 2012, 7, 359–374. [Google Scholar]
- Härd, T.; Lendel, C. Inhibition of amyloid formation. J. Mol. Biol 2012, 421, 441–465. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, K.A.; Rochet, J.C.; Bieganski, R.M.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Kinetic stabilization of the alpha-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-alpha-synuclein adduct. Science 2001, 294, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Manning-Bog, A.B.; Di Monte, D.A.; Fink, A.L. Dopamine and L-dopa disaggregate amyloid fibrils: implications for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 2004, 18, 962–964. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Rajamani, S.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Rifampicin inhibits alpha-synuclein fibrillation and disaggregates fibrils. Chem. Biol 2004, 11, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Rajamani, S.; Kaylor, J.; Han, S.; Zhou, F.; Fink, A.L. The flavonoid Baicalein inhibits fibrillation of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates existing fibrils. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 26846–26857. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, M.; Suzuki, N.; Taniguchi, S.; Oikawa, T.; Nonaka, T.; Iwatsubo, T.; Hisanaga, S.; Goedert, M.; Hasegawa, M. Small molecule inhibitors of alpha-synuclein filament assembly. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 6085–6094. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Yamada, M. Antioxidant compounds have potent anti-fibrillogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects for alpha-synuclein fibrils in vitro. J. Neurochem 2006, 97, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Yamada, M. Vitamin A potently destabilizes preformed alpha-synuclein fibrils in vitro: implications for Lewy body diseases. Neurobiol. Dis 2007, 25, 446–454. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnhoefer, D.E.; Bieschke, J.; Boeddrich, A.; Herbst, M.; Masino, L.; Lurz, R.; Engemann, S.; Pastore, A.; Wanker, E.E. EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2008, 15, 558–566. [Google Scholar]
- McKoy, A.F.; Chen, J.; Schupbach, T.; Hecht, M.H. Novel inhibitor of amyloid β (Aβ) peptide aggregation: from high throughput screening to efficacy in an animal model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 38992–39000. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberto, G.R.; Torres-Monserrat, V.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Salvatella, X.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernández, C.O. Toward the discovery of effective polycyclic inhibitors of alpha-synuclein amyloid assembly. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 32036–32044. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Abedini, A.; Plesner, A.; Middleton, C.T.; Potter, K.J.; Zanni, M.T.; Verchere, C.B.; Raleigh, D.P. The sulfated triphenyl methane derivative acid fuchsin is a potent inhibitor of amyloid formation by human isletamyloid polypeptide and protects against the toxic effects of amyloid formation. J. Mol. Biol 2010, 400, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Abedini, A.; Plesner, A.; Verchere, C.B.; Raleigh, D.P. The flavanol (−)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide, disaggregates amyloid fibrils, and protects cultured cells against IAPP-induced toxicity. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8127–8133. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Minoda, K.; Kusaka, K.; Ito, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Akagawa, M.; Mochizuki, K.; Goda, T.; Nakayama, T. Human serum albumin as an antioxidant in the oxidation of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate: participation of reversible covalent binding for interaction and stabilization. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem 2011, 75, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kim, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Han, S.; Nakamura, C.; Ikebukuro, K.; Sode, K. Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) prevents fibril formation of alpha-synuclein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2006, 349, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Fukuda, M.; Ogasawara, D.; Kobayashi, N.; Han, S.; Nakamura, C.; Inada, M.; Miyaura, C.; Ikebukuro, K.; et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone inhibits the fibrillation of amyloid proteins. Prion 2010, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Kim, J.; Ikebkuro, K.; Sode, K. The inhibition of amyloid fibrillation using the proteolytic products of PQQ-modified α-synuclein. Open Biotechnol. J 2009, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Heise, H.; Hoyer, W.; Becker, S.; Andronesi, O.C.; Riedel, D.; Baldus, M. Molecular-level secondary structure, polymorphism, and dynamics of full-length alpha-synuclein fibrils studied by solid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15871–15876. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Margittai, M.; Chen, J.; Langen, R. Investigation of alpha-synuclein fibril structure by site-directed spin labeling. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 24970–24979. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar, M.; Chou, H.T.; Lührs, T.; Maji, S.K.; Riek-Loher, D.; Verel, R.; Manning, G.; Stahlberg, H.; Riek, R. The fold of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8637–8642. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrih, N.P.; Barry, C.H.; Fink, A.L. Impact of Tyr to Ala mutations on alpha-synuclein fibrillation and structural properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gattiker, A.; Bienvenut, W.V.; Bairoch, A.; Gasteiger, E. FindPept, A tool to identify unmatched masses in peptide mass fingerprinting protein identification. Proteomics 2002, 2, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. PuProtein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; A product of Humana Press: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Yoshiike, Y.; Takashima, A.; Hasegawa, K.; Naiki, H.; Yamada, M. Vitamin A exhibits potent antiamyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects in vitro. Exp. Neurol 2004, 189, 380–392. [Google Scholar]
| Position | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 3–13 | VFMKGLSKAKE |
| 21–28 | KTKQGVAE |
| 36–46 | GVLYVGSKTKE |
| 47–57 | GVVHGVATVAE |
| 127–131 | MPSEE |
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, W.; Kobayashi, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Ikebukuro, K.; Sode, K. Partial Peptide of α-Synuclein Modified with Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Inhibits Amyloid Fibrillation of α-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2590-2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14022590
Yoshida W, Kobayashi N, Sasaki Y, Ikebukuro K, Sode K. Partial Peptide of α-Synuclein Modified with Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Inhibits Amyloid Fibrillation of α-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(2):2590-2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14022590
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Wataru, Natsuki Kobayashi, Yasuhiko Sasaki, Kazunori Ikebukuro, and Koji Sode. 2013. "Partial Peptide of α-Synuclein Modified with Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Inhibits Amyloid Fibrillation of α-Synuclein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 2: 2590-2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14022590
APA StyleYoshida, W., Kobayashi, N., Sasaki, Y., Ikebukuro, K., & Sode, K. (2013). Partial Peptide of α-Synuclein Modified with Small-Molecule Inhibitors Specifically Inhibits Amyloid Fibrillation of α-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(2), 2590-2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14022590





